ELZU 30 X&Y-Axis WAC
Modular Linear Actuator, External Roller Bearing Guided, External Belt Driven, Model ELZU, X and Y Axis Wrap Around Carriage, 30
Read More
Product Specifications
Product Specifications
Configure

Product Specifications
Details
- Size:
- 30
- Belt:
- 3M12
- mm/Rev:
- 75
- Number of Teeth:
- 25
Dimensions
- Basic length Lx [mm]:
- 252
- Basic length Ly [mm]:
- 222
- A [mm]:
- 70
- B [mm]:
- 56
- C [mm]:
- 42
- D [mm]:
- 28
- E [mm]:
- 13
- F [mm]:
- 25
- G [mm]:
- -
- H [mm]:
- -
- I [mm]:
- 27
- J [mm]:
- 44
- K [mm]:
- 47
- MM:
- -
- N:
- M5
- OO:
- M6
- P [mm]:
- 36
- Qx [mm]:
- 94
- Qy [mm]:
- 138
- T:
- M5
- V [mm]:
- 74
- X [mm]:
- 16
- Y [mm]:
- 16
- Shaft Diameter and Length [mm]:
- 6 x 15
- Key:
- 2x2x12
Speed
- Speed Maximum [m/s]:
- 2
Forces and Torques
- No-load torque [Nm]:
- 0.2
- Tensile force 0.2 sec [N]:
- 280
- Tensile force permanent [N]:
- 200
- Fx dynamic [N]:
- 180
- Fy dynamic [N]:
- 60
- Fz dynamic [N]:
- 60
- Mx dynamic [Nm]:
- 5
- My dynamic [Nm]:
- 6
- Mz dynamic [Nm]:
- 7
- Fx static [N]:
- 200
- Fy static [N]:
- 90
- Fz static [N]:
- 90
- Mx static [Nm]:
- 10
- My static [Nm]:
- 13
- Mz static [Nm]:
- 14
Geometrical moments of inertia of aluminum profile
- Elastic modulus [N/mm2]:
- 70000
- lx [mm4]:
- 40900
- ly [mm4]:
- 40900
Weight
- Additional Weight per 100 mm [kg]:
- 0.13
- Basic Weight [kg]:
- 6.3
Values for Calulating Inertias
- Pulley Material:
- Steel
- Pulley Diameter [mm]:
- 23.87
- Effective Pulley Width [mm]:
- 42.0
- Belt Weight [kg/m]:
- 0.037
- Standard Carriage Weight [kg]:
- 0.35
- No-load torque [Nm]:
- 0.2
- Friction Coefficient:
- 0.01
More Details
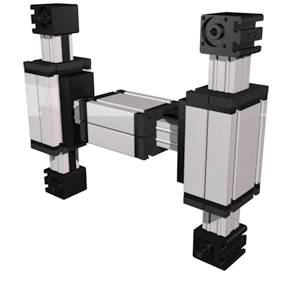
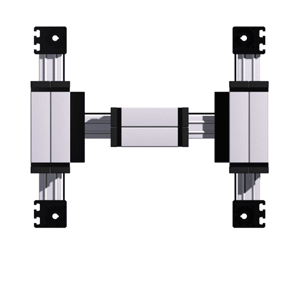
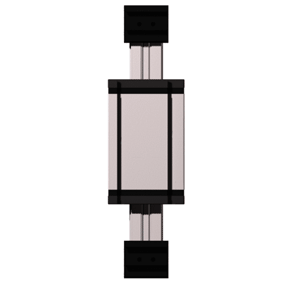
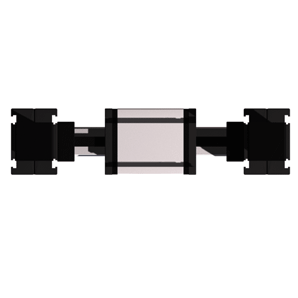
The carriage is driven by an external linear belt that can be adjusted to reduce lash and is driven along the external roller bearings. The pulleys have maintenance-free ball bearings. Belt tension can be readjusted by a simple screw adjustment device in the carriage.
The ELZU consisting of two Y-axes and single X-axis, driven by one rotating belt. This belt runs around different deflection pulleys. Positioning is achieved by two motors. The coordinate is diagonal to the deflection points of the Y-axis. Advantage: A smaller amount of inertia is needed, thus enabling high accelerations to be achieved.